Food and Beverage Services NC II

COURSE DESIGN
|
SUBJECT TITLE: |
FOOD AND BEVERAGE SERVICES NC II |
|
NOMINAL DURATION: |
160 HOURS |
|
SUBJECT DESCRIPTION: |
This course is designed to enhance the knowledge, skills and attitude in FOOD AND BEVERAGE SERVICES NC II in accordance with industry standards. It covers core competencies on cleaning bar areas, operating a bar, preparing and mixing of cocktails, providing link between kitchen and service areas, providing room service, providing food and beverage service, developing and updating of food and beverage knowledge and providing wine services. |
|
STUDENT ENTRY REQUIREMENTS: |
Student must possess the following qualifications, must be: · Able to communicate both oral and written. · Physically and mentally fit. · With good moral character. · Can perform basic mathematical and logical computations. · Analytical and logical thinking. |
COURSE STRUCTURE
|
Lesson 1: Introduction Food and Beverage Services Nominal Hours: 5 |
||
|
L.O. 1.1 |
Definition and Evolution of Food and Beverage Services |
|
|
L.O. 1.2 |
Types and Sectors of Food Service Industry |
|
|
L.O. 1.3 |
Food Service Method |
|
|
L.O. 1.4 |
Restaurant Service |
|
|
L.O. 1.5 |
Restaurant Lay-out |
|
|
Lesson 2: Organization and Responsibilities of Food and Beverage Operation Nominal Hours: 5 |
||
|
L.O. 2.1 |
Organizational Chart of Food and Beverage Industry |
|
|
L.O. 2.2 |
Associated Departments of Hotel Food Service |
|
|
L.O. 2.3 |
Professional Ethics for Good Food Service Personnel |
|
|
Lesson 3: Restaurant Equipment, Supplies and Table Appointments Nominal Hours: 10
|
||
|
L.O. 3.1 |
Service Equipment and Supplies in Restaurant Service |
|
|
L.O. 3.2 |
Table Appointments |
|
|
L.O. 3.3 |
Sanitation and Safety standards in handling food service equipment |
|
|
Lesson 4: Menu Nominal Hours: 5 Learning Objective: |
||
|
L.O. 4.1 |
Definition of Menu |
|
|
L.O. 4.2 |
Structure of the Menu |
|
|
L.O. 4.3 |
Basic categories of menu |
|
|
L.O. 4.4 |
Menu Planning |
|
|
L.O. 4.5 |
Menu Format |
|
|
Lesson 5: Art of Napery Nominal Hours: 15 |
||
|
L.O. 5.1 |
Basic Napkin Folds |
|
|
L.O. 5.2 |
Flat Napkin Folds |
|
|
L.O. 5.3 |
Standing Napkin Folds |
|
|
L.O. 5.4 |
Object/Dependent Napkin Folds |
|
|
Lesson 6: Table Skirting Nominal Hours: 15 |
||
|
L.O. 6.1 |
Styles of Table Skirting |
|
|
Lesson 7: Tray and plate handling technique Nominal Hours: 10 |
||
|
L.O. 7.1 |
Plate Carrying |
|
|
L.O. 7.2 |
Tray Carrying |
|
|
L.O. 7.3 |
Unloading Tray |
|
|
Lesson 8: Table lay-out and setup Nominal Hours: 15 |
||
|
L.O. 8.1 |
Standards of Table Setup |
|
|
L.O. 8.2 |
Set-up Procedures |
|
|
L.O. 8.3 |
Types pf Table Set-up |
|
|
Lesson 9: Pre-meal Service Nominal Hours: 15 |
||
|
L.O. 9.1 |
Mise-en-place |
|
|
L.O. 9.2 |
Errands for Food Service Preparation |
|
|
L.O. 9.3 |
Restaurant reservation |
|
|
Lesson 10: Sequence of Table Service Nominal Hours: 45 |
||
|
L.O. 10.1 |
Meet and greet guest |
|
|
L.O. 10.2 |
Escorting and seating customer |
|
|
L.O. 10.3 |
Offering pre-meal services |
|
|
L.O. 10.4 |
Presenting menus and drink list |
|
|
L.O. 10.5 |
Take food and beverage orders |
|
|
L.O. 10.6 |
Transfer orders to kitchen for service |
|
|
L.O. 10.7 |
Adjust settings and covers |
|
|
L.O. 10.8 |
Serve foods |
|
|
L.O. 10.9 |
Serve drinks |
|
|
L.O. 10.10 |
Present accounts to guest |
|
|
Lesson 11: Room Service Nominal Hours: 20 |
||
|
L.O. 11.1 |
Definition of room service |
|
|
L.O. 11.2 |
Kinds of room service |
|
|
L.O. 11.3 |
Take guest room service order |
|
|
L.O. 11.4 |
Set-up trays/trolley for room service |
|
|
L.O. 11.5 |
Delver room service order |
|
|
L.O. 11.6 |
Present room service |
|
|
L.O. 11.7 |
Clear room service |
|
1. Lesson 1: Introduction of Food and Beverage Service
|
1.1 Food and Beverage Service
- It is the climax of the relationship between a customer and a caterer during a meal experience.
- The actual contact with the customer is made at this stage of the food and beverage operation.
- The food and beverage department has three main operation areas, they are:
1. Food Production (Kitchen/Bakery)
2. Bar (Beverage)
3. Restaurant (Service)
Evolution of Food Service Industry
- The first encounters in the food and beverage service were recorded in the holy book. The stories of Abraham when he entertained angels in Mamre (Genesis 18:1-8) and Lot in Sodom when he met the same angels (Genesis 19:1-3).
- During the early times, medieval period, renaissance period and industrialized period, people always seek travel and accommodation. In every place people go, they dine and drink to harmonize with the society and environment.
- In the Philippines, the status quo of Food and Beverage Service started in three categories; the ‘Barrio Fiesta’, the ‘Town Fiesta’ and the ‘Provincial Events’.
- In the present day, Food Service Industry is divided in 2 main categories: Commercial Food Service Industry and Institutional Food Service Industry.
1.2 Types of Food Service Industry:
1. Commercial Food Service Industry
- It is a group of different food service establishments and is usually located in commercial or public areas especially in places where people are concentrated.
2. Institutionalized Food Service Industry
- It is made up of institutions or different institutions owning or operating food service establishment/s within their institutional boundaries in schools and hospitals.
3. Industrial Food Service Industry
- It is found in industrial areas or industrial parks where groups of different industrial manufacturing plants are concentrated. It caters to workers of different categories within its industrial boundaries.
Sectors of the food and beverage service industry
1. Hotels
- Provision of food and drink together with accommodation
2. Restaurants
- Provision of food and drink generally at medium to high price with medium to high levels of service
3. Catering
- Provision of food and drink generally at low to medium price with limited levels of service
4. Fast food
- Provision of food and drink in highly specialized environment characterized by high investment, high labor costs and vast customer throughput.
5. Take-away
- Provision of food and drinks quickly
6. Functions (banqueting/conferences/convention/exhibitions)
- Provision of food and drink on large-scale, usually pre-booked
7. Motorway service stations
- Provision of food together with retail and petrol services for motorway travelers.
8. Leisure attraction
- Provision of food and drink for people engaged in another leisure pursuit
9. Welfare (hospital/schools/colleges/universities/prisons/forces)
- Provision of food and drink to people through social need, primarily determined by an authority, social conscience
10. Industrial catering (in-house catering)
- Provision of food and drink to people at work
11. Transport
- Provision of food and drink to people on the move
1.3 FOOD AND BEVERAGE SERVICE METHODS
- The service of food and beverages may be carried out in many ways depending on a number of factors:
a. The type of establishment
b. The type of customer to be served
c. The time available for the meal
d. The turnover of custom expected
e. The type of menu presented
f. The cost of meal served
g. The site of the establishment
- There are 5 types of basic food and beverage method:
a. Table service- this is assisted by a waiter where the customer sits on his/her table and his/her food and beverage orders are served
b. Assisted service- a combination of waiter service and self-service where the food and beverage orders can be served by a waiter and at some point there are food and beverage items which are collected by the customer from a smorgasbord (open table with food and beverage items).
c. Self-service- the serving of oneself (as in a restaurant or gas station) with goods or services to be paid for at a cashier's desk or by using a coin-operated mechanism or a credit or debit card.
d. Single-point service- In this type of service, the guest orders, pays for his order and gets served all at a single point. There may be may not be any dining area or seats.
e. Specialized service- It is called special service because it provides food and beverage at the places which are not meant for food & beverage service.
1.4 Restaurant Service
Restaurant
- It is a food outlet that serves food and beverages to dine-in customers as differentiated from those being served in take-out counters or vending machines.
- It is a commercial establishment committed to the sale of food and beverage.
- It was derived from the Latin word, ‘resturare’ meaning ‘to restore’. It started when a soup vendor offered the King of France where the king was delighted to the soup he consumed. Through public commotion, the soup was merchandized as “le restaurant divin” (the divine restorative).
- A restaurant concept begins with an overview of marketing mix and market orientation. The main factors to be considered are:
a. The site is top priority as it determines the degree of contact or exposure to market
b. The size of the food and beverage operation determines the desired impact on the market
c. The menu is a fundamental aspect of the early decision-making process aimed to satisfying customer expectations.
d. Pricing policies determine the average spend and affect the sales volume
e. Service, in conjunction with the type of restaurant, menus, customers and seating arrangement
f. Opening hours, days according to marketing strategies and customer requirements
g. Décor and music, for pleasant environment which contributes to customer satisfaction
h. Standards and quality, it is according to customer requirements
i. Advertising and merchandising, to appeal to the market segments
j. Meal functions
- The type of service and the service procedures among restaurants vary depending on their classification, the type of food and services, the volume of orders and the composition of their prospective customers.
- Dine-in restaurants come in various types like:
1. Coffee shop - A concept borrowed from the United States, distinguished by its quick service. Food is pre- plated in the kitchen. The chefs prepare complete and balanced meal arranged in a plate. Coffee shop menus are quite light and simple.
2. Fine dining restaurants - it is usually designed for the elite market and they serve special dishes of superior quality, often with elegance of wine service and sometimes table side preparation and gueridon service.
3. Specialty restaurants - In such restaurants, the entire atmosphere and décor is geared to a particular theme normally related to regional cuisine. Specialty restaurants have gone further in giving the public ethnic foods within a region. The global world is allowing investors to bring cuisines to an ever adventurous and knowledgeable guest profile building restaurants to around the cuisine.
4. Grill room or Rotisserie - This is a restaurant that specializes itself in grills of different meats, fish and poultry. The distinguishing feature of this type of restaurant is a glass partition that separates the kitchen from the dining area so that the guest can see the grill preparation of her choice.
5. Discotheque - It is a restaurant which is principally meant for dancing to recorded music. The music is driven by a qualified and expert DJ who creates or responds to the moods of the guests. Special lighting and a dance floor are essential to the discotheque. A feature of the discotheque is a bar which also offers light meals and finger snacks.
6. Fast Food Restaurant - Fast food restaurants have practically taken over the modern dining experience. Fast food restaurants give ready-to-serve foods at reasonable rates. The guest pays cash and carries the foods instantly.
7. Cafeteria - meant for people with low meal budget. It serves value meals that are usually displayed in fast food counter.
8. Bars - Bars are where liquors are sold and consumed. In some parts of Europe they called it INNS; while in U.K they are called PUBS and TAVERNS. Bars have to be licensed to serve liquor as they have to follow strict laws and rules like closing time, serving underage persons, observing dry days, etc.
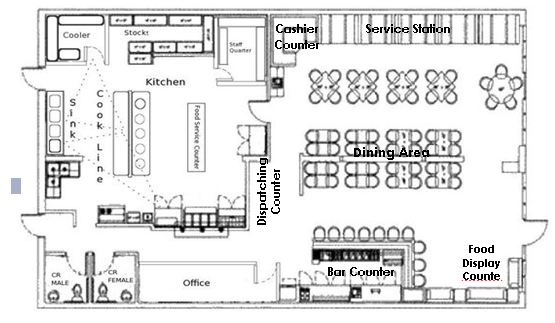
1.5 The Restaurant Layout
The restaurant layout must be designed to insure convenience of service to both service staffs and customers. The layout usually consists of:
1. Dining Area
For large restaurants with seating capacity of more than 100, and the orders come in big volume, it will be advisable to divide the dining area into stations with each station installed with 7-15 tables and about 30-50 seats. Each table must be given specific number for easy identification.
When a big dining area is split into smaller sub-areas or station, the span of control of a station head is smaller making supervision and monitoring or service more manageable and easier to control.
Each station (sub-area) is manned by a station head (or captain waiter), assisted by assigned waiters or food attendants. A busboy is assigned to each station and he acts as runner to the kitchen so that waiters can concentrate on order taking service, without having to leave their assigned station. For a more efficient delivery of service, waiters must be given specific table assignments.
2. Bar Counter
Restaurant serving drinks are advised to set up a bar counter where drink orders are placed and prepared. The bar area shall be equipped with a counter where various wines and drinks are displayed. The bar is manned by a bartender (if there are mixed drinks available) or a bar waiter who is in charge of drink preparation and dispatching. If there is a large volume of drink orders, a barboy may also be assigned to assist the bartender.
3. Food Display Counter
Restaurants serving buffet or fast foods or counter items usually set up a specific place for food display. This counter is manned by food dispatchers who must be in complete uniform, including hair net/cap, apron, gloves.
4. Dispatching Counter
The food from the kitchen must be dispatched through a window counter so that waiters need not to go to the kitchen to pick up and assemble orders. A food dispatcher is assigned to handle the dispatching of orders.
5. Cashier’s Counter
This is the area where the cashier is seated to attend to bill settlement. It must be equipped with a cash register or the Point of Sales System (POS), bill forms and receipts and other paraphernalia for cashiering.
6. Dishwashing Counter
The dishwashing area is placed inside the kitchen. However, there must be a window counter where soiled dishes will be placed by waiters, without having to enter the kitchen. Washed, cleaned wares will also be picked from this counter,
7. Service Station or Side Stand
This area is the place where preparations for service are undertaken. The station is equipped with sideboard or cabinet with drawers for placing the par stock of supplies, cutleries, condiments and service equipment to be used for set up and service.
8. Food Preparation Area (Kitchen)
The food preparation area must be located at the back or adjacent to the dining area so that the dispatching orders will be faster and more efficient.
Sample Restaurant Lay-out Plan
Restaurant brigade
- The manning requirements for each restaurant or any food outlet depend on the type of service and the volume of orders
- The required number of waiters or servers is usually calculated based on the productivity standard (number of covers or guest that a waiter can serve within a meal period). The standard varies for each type of service and the capacity of the dining personnel.
- Below-mentioned is the typical productivity ration used by large and medium-sized food establishment:
· 1 waiter/attendant for every 15 customers (American or Plate Service)
· 1 waiter for every table for 10-12 customers (Russian Service)
· 1 waiter for every 5 customers (French Service with side-table preparation
· 1 waiter for every 20-25 customers (Buffet Service)
· 1 waiter for every 20-25 customers or 4-5 tables (Family or Lauriat Service)